Dorothy Bonvillion, a prominent figure in the field of early childhood education, is an American educator and researcher who dedicated her career to advocating for the significance of play in children's learning and development.
Throughout her extensive career, Bonvillion has consistently emphasized the crucial role of play in fostering children's cognitive, emotional, and social well-being. Her research and advocacy have significantly influenced early childhood education practices, highlighting the importance of play-based learning environments that nurture children's natural curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
Bonvillion's work has not only shaped the understanding of play in early childhood education but has also influenced broader educational policies and practices. Her dedication to promoting the value of play has contributed to a deeper appreciation of the importance of holistic child development, recognizing the vital role of play in children's overall growth and well-being.
Dorothy Bonvillion
Dorothy Bonvillion, an influential figure in early childhood education, is known for her dedication to play-based learning. Here are eight key aspects of her work:
- Advocate for play: Bonvillion consistently emphasized the importance of play in children's learning and development.
- Research on play: Her research explored the cognitive, emotional, and social benefits of play.
- Influence on policy: Her work influenced early childhood education practices and policies.
- Holistic development: Bonvillion recognized the role of play in children's overall growth and well-being.
- Early childhood education: She dedicated her career to promoting play in early childhood settings.
- Curiosity and creativity: Play-based learning environments foster children's natural curiosity and creativity.
- Problem-solving: Play helps children develop problem-solving abilities.
- Social interaction: Play promotes social interaction and cooperation among children.
In conclusion, Dorothy Bonvillion's work highlights the essential role of play in children's learning and development. Her research and advocacy have shaped early childhood education practices, recognizing the importance of play-based environments that nurture children's cognitive, emotional, and social well-being. Bonvillion's legacy continues to inspire educators and policymakers to prioritize play in children's lives, ensuring that they have the opportunities to learn, grow, and thrive through play.
Advocate for play
Dorothy Bonvillion, an influential figure in early childhood education, dedicated her career to advocating for the significance of play in children's learning and development. Her unwavering belief in the power of play led her to consistently emphasize its importance in fostering children's cognitive, emotional, and social well-being.
Bonvillion's research and advocacy have significantly contributed to the understanding of play in early childhood education. Her work has highlighted the crucial role of play-based learning environments that nurture children's natural curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving abilities. By emphasizing the importance of play, Bonvillion has influenced educational policies and practices, ensuring that play is recognized as an essential component of children's learning and development.
In conclusion, Dorothy Bonvillion's unwavering advocacy for play has shaped the field of early childhood education. Her dedication to promoting the value of play has contributed to a deeper appreciation of its importance in children's overall growth and development. Bonvillion's legacy continues to inspire educators and policymakers to prioritize play in children's lives, ensuring that they have the opportunities to learn, grow, and thrive through play.
Research on play
Dorothy Bonvillion's research on play has significantly contributed to the understanding of its cognitive, emotional, and social benefits in children's development. Her work has provided a strong foundation for advocating the importance of play-based learning environments that nurture children's natural curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
Bonvillion's research has shown that play promotes cognitive development by enhancing children's attention, memory, and language skills. It also contributes to their emotional development by helping them regulate their emotions, develop self-awareness, and build resilience. Furthermore, play fosters social development by providing opportunities for children to interact with peers, learn cooperation, and develop empathy.
The practical significance of Bonvillion's research lies in its implications for early childhood education practices. By highlighting the benefits of play, her work has influenced the design of play-based curricula and the training of early childhood educators. This has led to a greater recognition of the importance of play in children's overall development and well-being.
Influence on policy
Dorothy Bonvillion's work on the importance of play in early childhood education has had a significant impact on policy and practice. Her research and advocacy have contributed to a growing recognition of the value of play-based learning environments that nurture children's cognitive, emotional, and social development.
As a result of Bonvillion's influence, many early childhood education policies and practices have been revised to incorporate more play-based activities. For example, the Head Start program, a federally funded preschool program for low-income families, has adopted play-based learning as a core component of its curriculum. Additionally, many states have adopted early learning standards that emphasize the importance of play in children's development.
The practical significance of Bonvillion's work lies in its implications for children's learning and well-being. Research has shown that children who participate in play-based learning environments have better cognitive, emotional, and social outcomes than children who do not. For example, children who participate in play-based learning environments have been shown to have better problem-solving skills, language skills, and social skills than children who do not. Additionally, play-based learning environments have been shown to promote children's creativity, imagination, and resilience.
Holistic development
Dorothy Bonvillion's recognition of the role of play in children's overall growth and well-being is a fundamental aspect of her work on early childhood education. She understood that play is notly a form of entertainment, but rather an essential component of children's development. Play provides children with opportunities to learn and grow in all areas, including cognitive, emotional, social, and physical development.
Bonvillion's research showed that play helps children develop their problem-solving skills, language skills, and social skills. She also found that play promotes children's creativity, imagination, and resilience. In addition, play helps children to regulate their emotions and develop self-awareness.
The practical significance of Bonvillion's work on holistic development is that it has helped to change the way that we think about play in early childhood education. It is now widely recognized that play is an essential part of children's learning and development. As a result, many early childhood education programs have adopted play-based learning approaches.
Early childhood education
Dorothy Bonvillion's dedication to promoting play in early childhood settings is a significant aspect of her work on early childhood education. She recognized the crucial role that play plays in children's overall development and well-being, and she advocated for its inclusion in early childhood education programs.
- Cognitive development: Play provides children with opportunities to learn and practice new skills, such as problem-solving, language, and social skills. It also helps them develop their creativity and imagination.
- Emotional development: Play helps children to regulate their emotions and develop self-awareness. It also provides them with opportunities to express themselves and to learn how to cope with stress.
- Social development: Play helps children to develop social skills, such as cooperation, communication, and empathy. It also provides them with opportunities to learn how to interact with others and to resolve conflicts.
- Physical development: Play helps children to develop their gross and fine motor skills. It also provides them with opportunities to get exercise and to learn about their bodies.
Bonvillion's work on early childhood education has had a significant impact on the field. Her research and advocacy have helped to change the way that we think about play in early childhood settings. It is now widely recognized that play is an essential part of children's learning and development. As a result, many early childhood education programs have adopted play-based learning approaches.
Curiosity and creativity
Dorothy Bonvillion, a leading advocate for play-based learning, recognized the crucial role that curiosity and creativity play in children's development. She believed that play provides children with opportunities to explore their interests, experiment with new ideas, and develop their imaginations. Bonvillion's research showed that children who engage in play-based learning are more likely to be curious and creative than children who do not.
In play-based learning environments, children are encouraged to ask questions, take risks, and learn from their mistakes. They are given the freedom to explore their interests and to develop their own ideas. This type of learning environment fosters creativity and innovation.
The practical significance of this understanding is that it helps educators to create learning environments that are more conducive to children's learning and development. By providing children with opportunities to play and explore, educators can help them to develop their curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving
Dorothy Bonvillion's research has shown that play is essential for the development of problem-solving abilities in children. Play provides children with opportunities to practice making decisions, taking risks, and learning from their mistakes. This type of learning is crucial for children's cognitive development, as it helps them to develop the skills they need to solve problems and make decisions in the real world.
- Decision-making: Play provides children with opportunities to make decisions, both big and small. For example, they may need to decide what game to play, what role to take on, or how to build a structure. Making these decisions helps children to develop their critical thinking skills and their ability to weigh the pros and cons of different options.
- Risk-taking: Play also provides children with opportunities to take risks. For example, they may need to climb a tree, jump off a swing, or try a new game. Taking these risks helps children to develop their confidence and their ability to persevere in the face of challenges.
- Learning from mistakes: Play is also a great way for children to learn from their mistakes. For example, they may build a tower that collapses or try a game that they can't win. Making these mistakes helps children to develop their problem-solving skills and their ability to learn from their experiences.
Bonvillion's research on the connection between play and problem-solving has had a significant impact on the field of early childhood education. Her work has helped to show the importance of play in children's development, and it has led to the development of new play-based learning programs that are designed to help children develop their problem-solving skills.
Social interaction
Dorothy Bonvillion's research has shown that play is essential for the development of social skills in children. Play provides children with opportunities to interact with peers, learn how to cooperate, and develop empathy.
- Peer interaction: Play provides children with opportunities to interact with peers from different backgrounds and with different skills and interests. This type of interaction helps children to develop their social skills, such as communication, cooperation, and empathy.
- Cooperation: Play often requires children to cooperate with each other in order to achieve a common goal, such as building a fort or playing a game. This type of cooperation helps children to develop their problem-solving skills and their ability to work together as a team.
- Empathy: Play also provides children with opportunities to develop empathy, or the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. For example, when children play pretend, they may take on the role of a character who is experiencing a different emotion, such as sadness or joy. This type of play helps children to develop their ability to understand and empathize with others.
- Social problem-solving: Play also provides children with opportunities to practice social problem-solving skills. For example, children may need to negotiate with each other over the rules of a game or resolve a conflict between two friends. This type of practice helps children to develop their ability to solve social problems and to interact with others in a positive way.
Bonvillion's research on the connection between play and social interaction has had a significant impact on the field of early childhood education. Her work has helped to show the importance of play in children's development, and it has led to the development of new play-based learning programs that are designed to help children develop their social skills.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dorothy Bonvillion
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions regarding Dorothy Bonvillion's work and its implications for early childhood education.
Question 1: What is Dorothy Bonvillion's primary contribution to the field of early childhood education?
Answer: Dorothy Bonvillion is renowned for her unwavering advocacy for the significance of play in children's learning and development. Her research and advocacy have significantly influenced early childhood education practices, highlighting the crucial role of play-based environments in fostering children's cognitive, emotional, and social well-being.
Question 2: How does play contribute to children's cognitive development?
Answer: Play enhances children's cognitive development by improving their attention, memory, and language skills. It also stimulates their creativity, imagination, and problem-solving abilities.
Question 3: What is the role of play in children's emotional development?
Answer: Play provides children with opportunities to regulate their emotions, develop self-awareness, and build resilience. It also helps them to express themselves and to learn how to cope with stress.
Question 4: How does play promote children's social development?
Answer: Play helps children to develop social skills, such as cooperation, communication, and empathy. It also provides them with opportunities to learn how to interact with others and to resolve conflicts.
Question 5: What are the implications of Bonvillion's work for early childhood education practices?
Answer: Bonvillion's research and advocacy have led to a greater recognition of the importance of play in children's overall development and well-being. As a result, many early childhood education programs have adopted play-based learning approaches.
Question 6: How can educators incorporate play into their early childhood education programs?
Answer: Educators can incorporate play into their programs by providing children with opportunities to engage in imaginative play, physical play, and social play. They can also use play to teach children about different concepts and skills.
In conclusion, Dorothy Bonvillion's work has significantly contributed to the understanding of the importance of play in children's development. Her research and advocacy have influenced early childhood education practices, emphasizing the crucial role of play-based environments in fostering children's cognitive, emotional, and social well-being.
Transition to the next article section: Dorothy Bonvillion's Legacy and Impact
Dorothy Bonvillion's Tips for Play-Based Learning
Dorothy Bonvillion, a leading advocate for play-based learning, has developed several research-based tips to help educators incorporate play into their early childhood education programs.
Tip 1: Provide children with opportunities for unstructured play.Unstructured play is play that is not directed by an adult. It allows children to use their imaginations and to explore their own interests. Research has shown that unstructured play is essential for children's cognitive, emotional, and social development.
Tip 2: Use play to teach children about different concepts and skills.Play can be used to teach children about a variety of concepts and skills, such as math, science, and language. For example, children can learn about shapes by playing with blocks, and they can learn about the solar system by playing with a model solar system.
Tip 3: Encourage children to play with a variety of materials.Providing children with a variety of materials to play with encourages them to explore their creativity and to develop their imagination. Different materials offer different opportunities for learning. For example, blocks can be used to build structures, while sand can be used to create sculptures.
Tip 4: Make sure that the play environment is safe and supportive.The play environment should be safe and supportive in order for children to feel comfortable and to be able to play freely. This means that the environment should be free of hazards, and it should be a place where children feel respected and valued.
Tip 5: Observe children's play and use it to inform your teaching.Observing children's play can help educators to understand their interests and their developmental needs. This information can then be used to inform teaching practices and to create a more supportive learning environment.
By following these tips, educators can create play-based learning environments that are both fun and educational. Play is essential for children's development, and it should be a part of every early childhood education program.
Conclusion: Dorothy Bonvillion's work has significantly contributed to the understanding of the importance of play in children's development. Her tips for play-based learning can help educators to create environments that are both fun and educational.
Conclusion
Dorothy Bonvillion's dedication to promoting the value of play in early childhood education has left an indelible mark on the field. Her unwavering advocacy and extensive research have profoundly influenced our understanding of the crucial role play plays in children's cognitive, emotional, and social development.
Bonvillion's work has not only shaped educational practices but has also sparked a broader recognition of the importance of play in children's overall well-being. Her legacy continues to inspire educators, policymakers, and parents alike to prioritize play in children's lives, ensuring that they have the opportunities to learn, grow, and thrive through play.
Unveiling The Cloud Frontier With Seven Cowboys Company
Unveiling The Multifaceted World Of Connie Izay: A Journey Of Talent And Impact
Unveiling The Enduring Bond: Marc Warren's Long-Term Partner Revealed
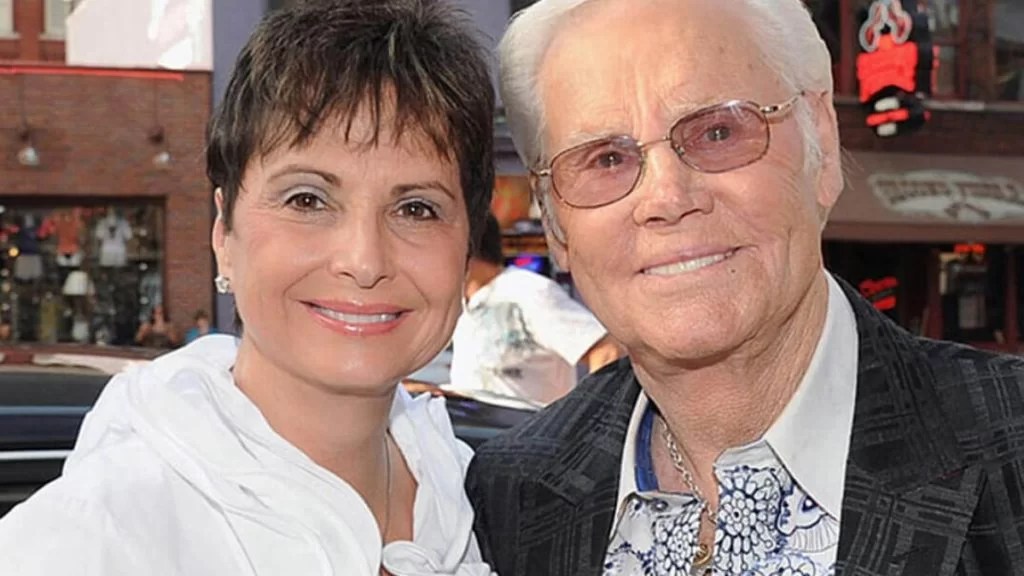

Dorothy Bonvillion Everything About Jones' ExWife Dicy Trends

Who is Jones wife Dorothy Bonvillion?
Dorothy Bonvillion's Biography, Wiki, Age, Height, Parents, Husband
ncG1vNJzZmiqkajAb7%2BSZ6ysZaeawLV5kWeYppmqpLuiw9JnmqilX5m8s7vTobBmmp%2Bjw6q4y6Kmp2aYqbqt